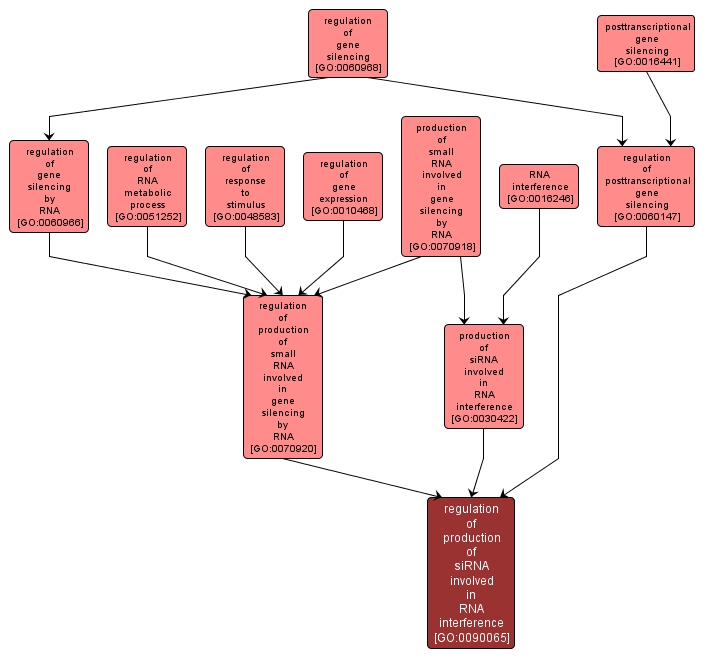
GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
regulation of production of siRNA involved in RNA interference |
| Acc: |
GO:0090065 |
| Aspect: |
Biological Process |
| Desc: |
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the production of siRNA, the cleavage of double-stranded RNA to form small interfering RNA molecules (siRNAs) of 21-23 nucleotides, in the context of RNA interference. |
Synonyms:
- regulation of RNA interference, production of siRNA
|
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|