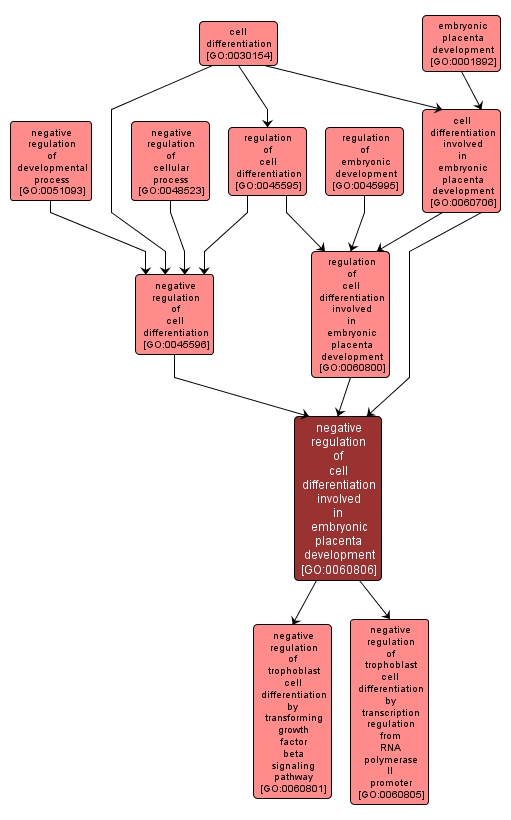
GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
negative regulation of cell differentiation involved in embryonic placenta development |
| Acc: |
GO:0060806 |
| Aspect: |
Biological Process |
| Desc: |
Any process that decreases the rate, frequency or extent of cell differentiation that contributes to the progression of the placenta over time, from its initial condition to its mature state. |
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|