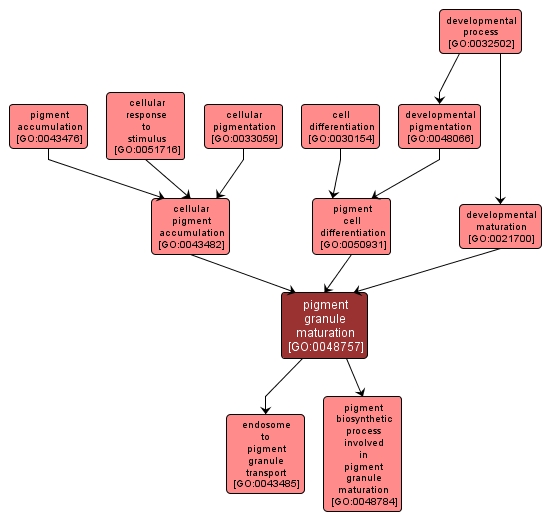
| Desc: |
Steps required to form a membrane-bounded organelle into a pigment granule containing pigment. Maturation is a developmental process, independent of morphogenetic (shape) change, that is required for a cell or structure to attain its fully functional state. |