GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
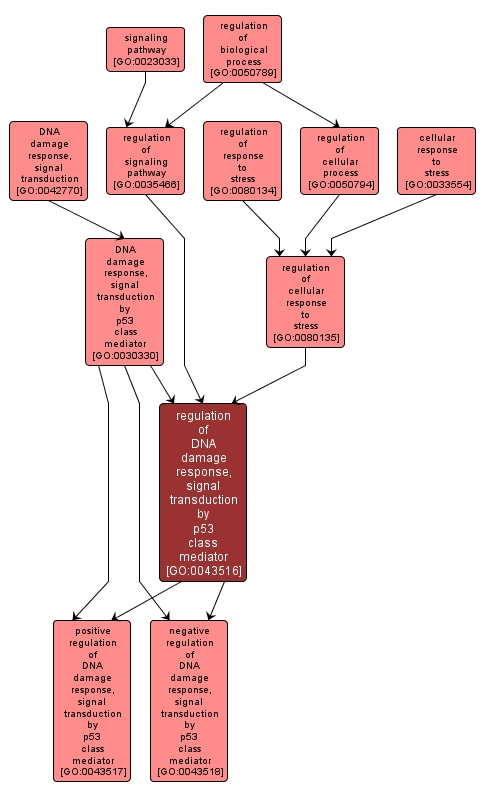
regulation of DNA damage response, signal transduction by p53 class mediator |
| Acc: |
GO:0043516 |
| Aspect: |
Biological Process |
| Desc: |
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the cascade of processes induced by the cell cycle regulator phosphoprotein p53, or an equivalent protein, in response to the detection of DNA damage. |
Synonyms:
- regulation of p53 induced by DNA damage response
|
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|