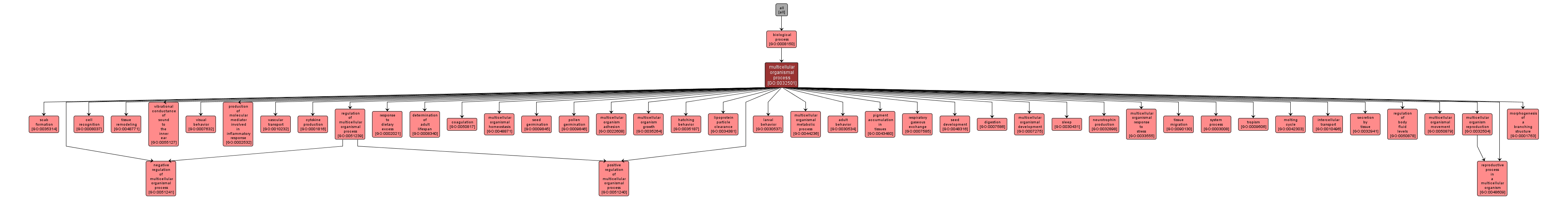
GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
multicellular organismal process |
| Acc: |
GO:0032501 |
| Aspect: |
Biological Process |
| Desc: |
Any biological process, occurring at the level of a multicellular organism, pertinent to its function. |
Synonyms:
- organismal physiological process
- GO:0050874
|
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|