GO TERM SUMMARY
|
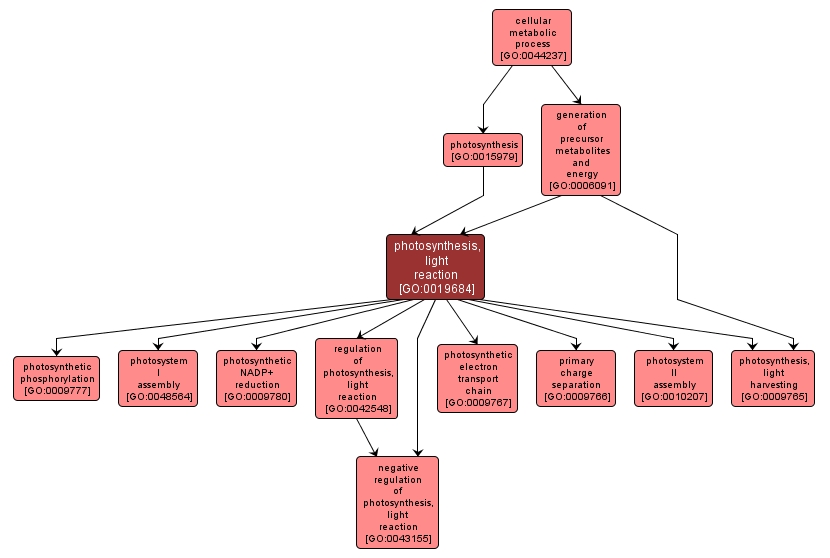
| Name: |
photosynthesis, light reaction |
| Acc: |
GO:0019684 |
| Aspect: |
Biological Process |
| Desc: |
The light reactions of photosynthesis, which take place in photosystems II and I. Light energy is harvested and used to power the transfer of electrons among a series of electron donors and acceptors. The final electron acceptor is NADP+, which is reduced to NADPH. NADPH generated from light reactions is used in sugar synthesis in dark reactions. Light reactions also generate a proton motive force across the thylakoid membrane, and the proton gradient is used to synthesize ATP. There are two chemical reactions involved in the light reactions: water oxidation in photosystem II, and NADP reduction in photosystem I. |
| Synonyms:
|
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|