| Desc: |
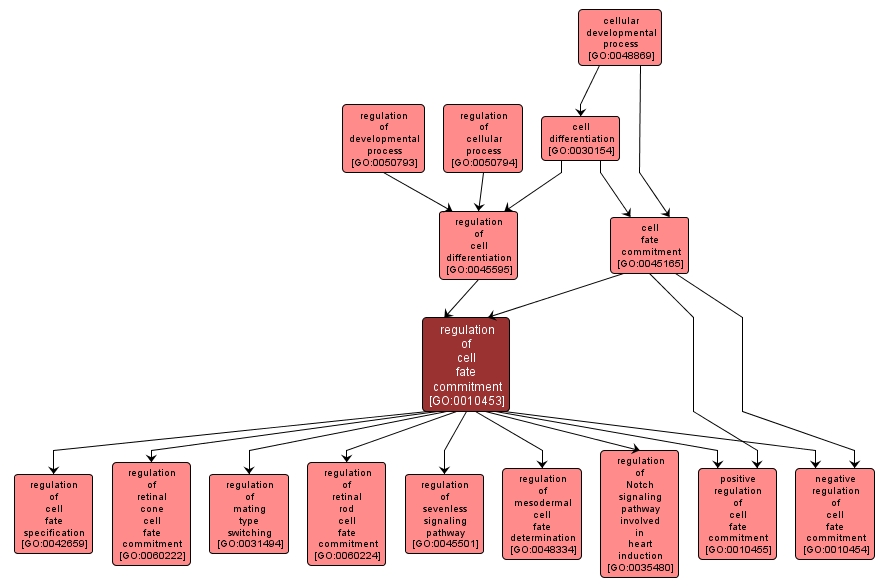
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of cell fate commitment. Cell fate commitment is the commitment of cells to specific cell fates and their capacity to differentiate into particular kinds of cells. Positional information is established through protein signals that emanate from a localized source within a cell (the initial one-cell zygote) or within a developmental field. |