GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
cohesin core heterodimer |
| Acc: |
GO:0008280 |
| Aspect: |
Cellular Component |
| Desc: |
The core heterodimer of a cohesin complex; a structure required for sister chromatid cohesion in eukaryotes. |
Synonyms:
- 9S cohesin
- Smc1-Smc3 complex
|
|

|
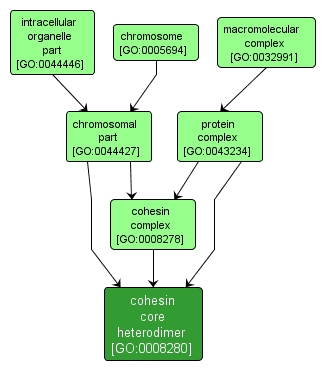
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|