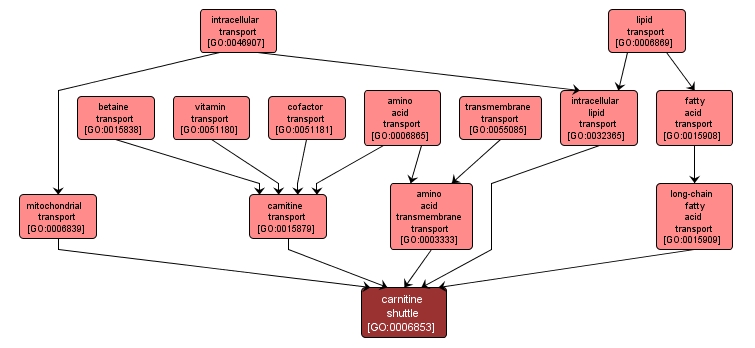
GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
carnitine shuttle |
| Acc: |
GO:0006853 |
| Aspect: |
Biological Process |
| Desc: |
The transfer of acyl groups to and from acyl-CoA molecules to form O-acylcarnitine, which can exchange across the mitochondrial inner membrane with unacylated carnitine. |
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|