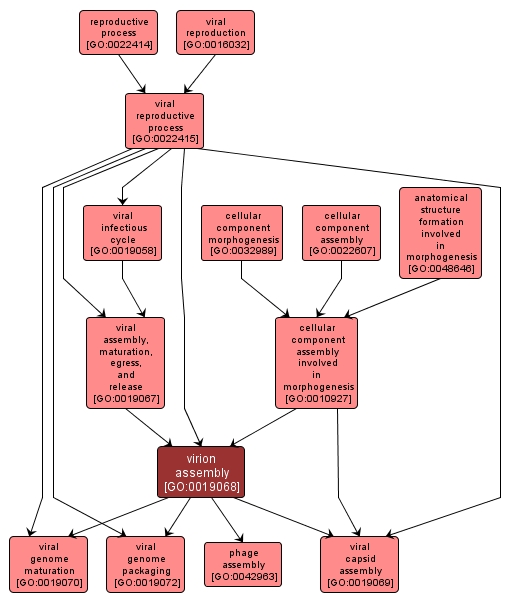
GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
virion assembly |
| Acc: |
GO:0019068 |
| Aspect: |
Biological Process |
| Desc: |
A late phase of viral replication during which all the components necessary for the formation of a mature virion collect at a particular site in the cell and the basic structure of the virus particle is formed. |
Synonyms:
- virus particle assembly
- viral particle assembly
- virus assembly
- viral assembly
|
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|