GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
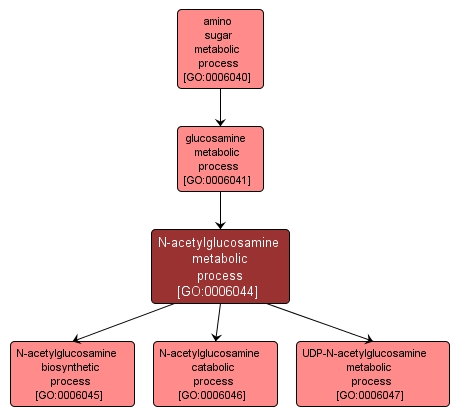
N-acetylglucosamine metabolic process |
| Acc: |
GO:0006044 |
| Aspect: |
Biological Process |
| Desc: |
The chemical reactions and pathways involving N-acetylglucosamine. The D isomer is a common structural unit of glycoproteins in plants, bacteria and animals; it is often the terminal sugar of an oligosaccharide moiety of a glycoprotein. |
Synonyms:
- N-acetylglucosamine metabolism
|
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|