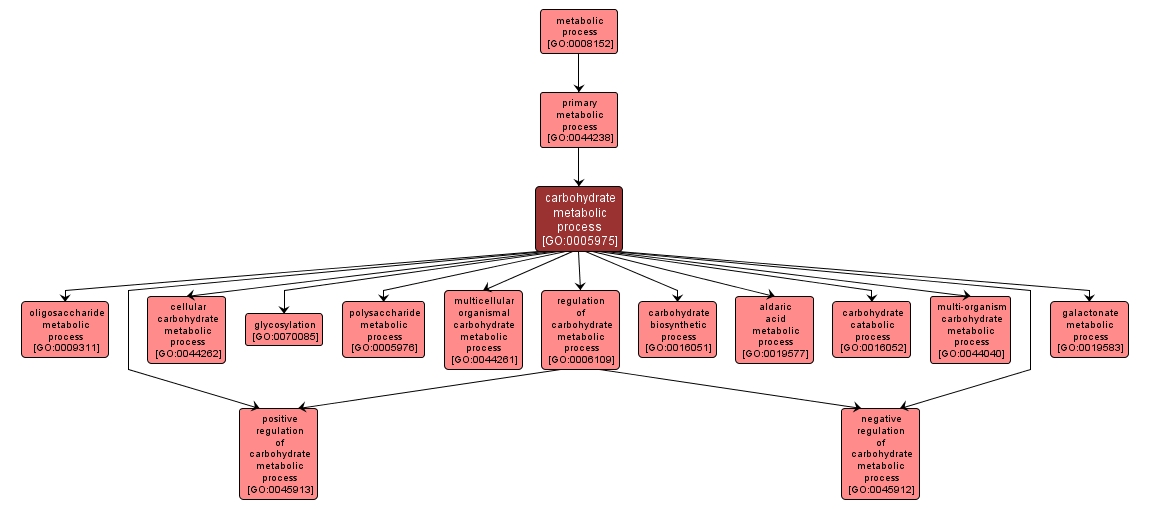
GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
carbohydrate metabolic process |
| Acc: |
GO:0005975 |
| Aspect: |
Biological Process |
| Desc: |
The chemical reactions and pathways involving carbohydrates, any of a group of organic compounds based of the general formula Cx(H2O)y. Includes the formation of carbohydrate derivatives by the addition of a carbohydrate residue to another molecule. |
| Synonyms:
|
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|