GO TERM SUMMARY
|
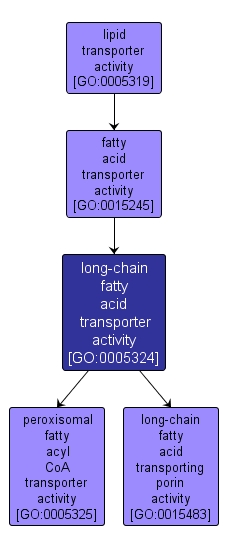
| Name: |
long-chain fatty acid transporter activity |
| Acc: |
GO:0005324 |
| Aspect: |
Molecular Function |
| Desc: |
Enables the directed movement of long-chain fatty acids into, out of, within or between cells. Long-chain fatty acids have a chain length of greater than 12 carbons. |
Synonyms:
- plasma membrane long-chain fatty acid transporter
|
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|