GO TERM SUMMARY
|
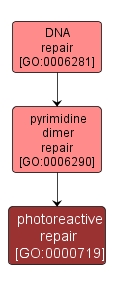
| Name: |
photoreactive repair |
| Acc: |
GO:0000719 |
| Aspect: |
Biological Process |
| Desc: |
The repair of UV-induced T-T, C-T and C-C dimers by directly reversing the damage to restore the original pyrimidines. |
Synonyms:
- pyrimidine-dimer repair by photolyase
|
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|