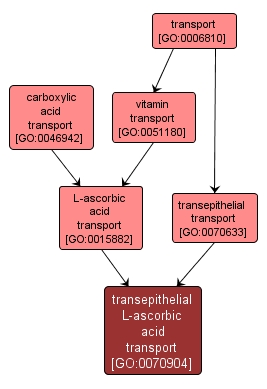
GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
transepithelial L-ascorbic acid transport |
| Acc: |
GO:0070904 |
| Aspect: |
Biological Process |
| Desc: |
The directed movement of L-ascorbic acid from one side of an epithelium to the other. |
Synonyms:
- transepithelial L-ascorbate transport
- transepithelial vitamin C transport
|
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|