| Desc: |
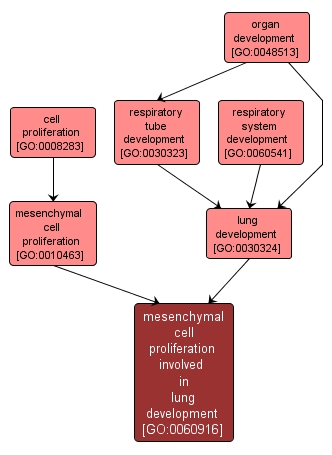
The multiplication or reproduction of cells, resulting in the expansion of a mesenchymal cell population that contributes to the progression of the lung over time. A mesenchymal cell is a cell that normally gives rise to other cells that are organized as three-dimensional masses, rather than sheets. |