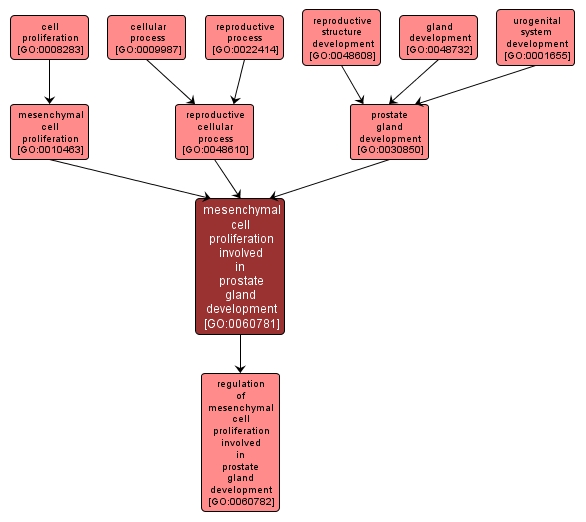
GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
mesenchymal cell proliferation involved in prostate gland development |
| Acc: |
GO:0060781 |
| Aspect: |
Biological Process |
| Desc: |
The multiplication or reproduction of mesenchymal cells, resulting in the expansion of a cell population that contributes to the progression of the prostate gland over time. |
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|