GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
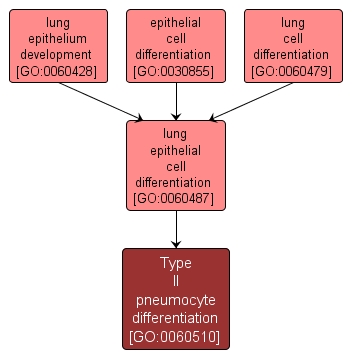
Type II pneumocyte differentiation |
| Acc: |
GO:0060510 |
| Aspect: |
Biological Process |
| Desc: |
The process whereby a relatively unspecialized cell acquires specialized features of a Type II pneumocyte. A Type II pneumocyte is a surfactant secreting cell that contains abundant cytoplasm containing numerous lipid-rich multilamellar bodies. |
Synonyms:
- granular pneumocyte differentiation
- large alveolar cell differentiation
- great alveolar cell differentiation
|