| Desc: |
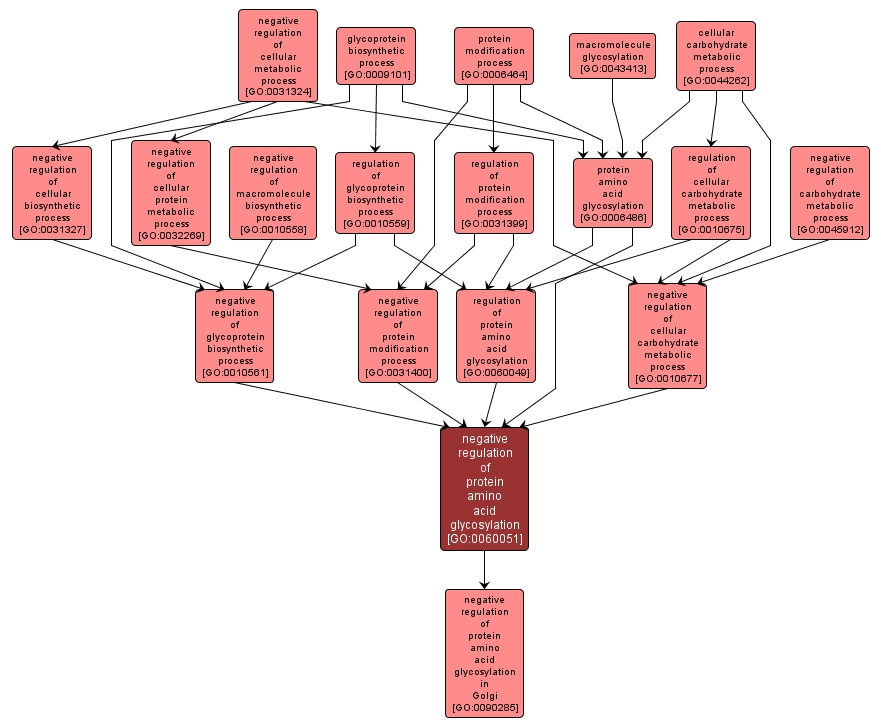
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of the glycosylation of one or more amino acid residues within a protein. Protein amino acid glycosylation is the addition of a sugar unit to a protein amino acid, e.g. the addition of glycan chains to proteins. |