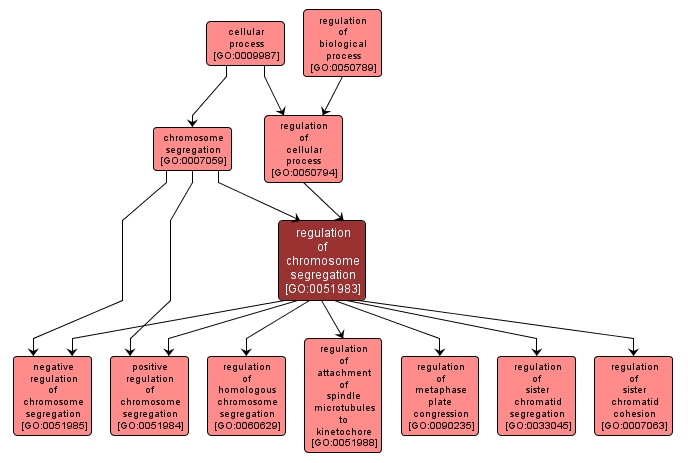
GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
regulation of chromosome segregation |
| Acc: |
GO:0051983 |
| Aspect: |
Biological Process |
| Desc: |
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of chromosome segregation, the process by which genetic material, in the form of chromosomes, is organized and then physically separated and apportioned to two or more sets. |
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|