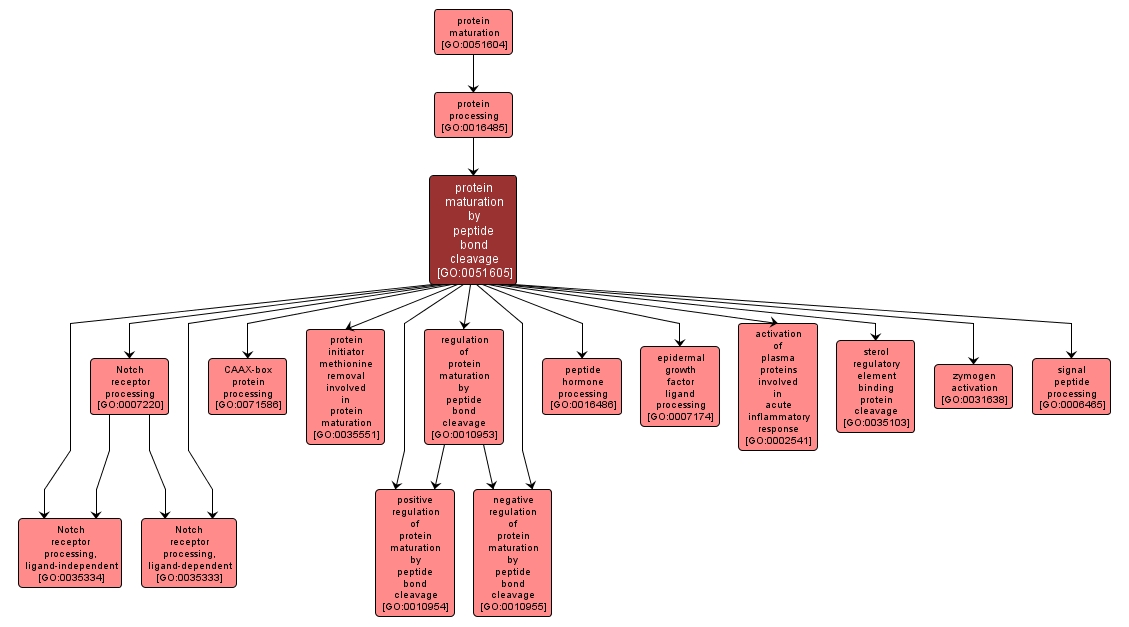
GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
protein maturation by peptide bond cleavage |
| Acc: |
GO:0051605 |
| Aspect: |
Biological Process |
| Desc: |
The hydrolysis of a peptide bond or bonds within a protein as part of protein maturation, the process leading to the attainment of the full functional capacity of a protein. |
Synonyms:
- protein maturation by proteolysis
- protein maturation by peptide bond hydrolysis
- peptidolysis during protein maturation
|
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|