| Desc: |
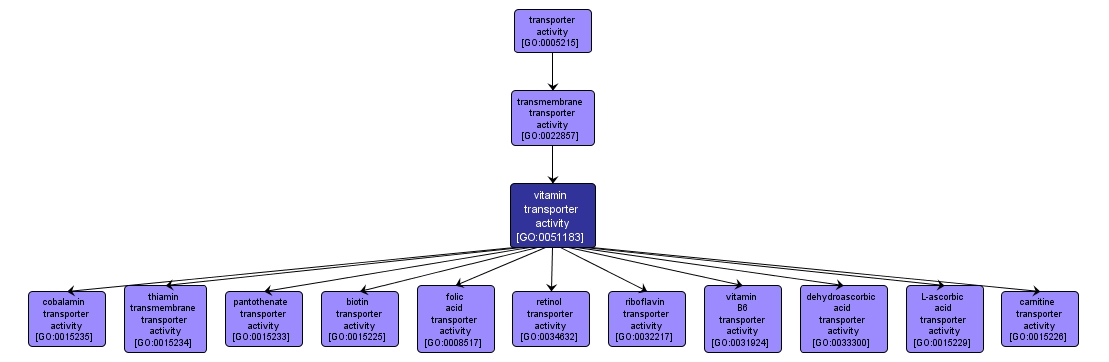
Enables the directed movement of vitamins into, out of, within or between cells. A vitamin is one of a number of unrelated organic substances that occur in many foods in small amounts and that are necessary in trace amounts for the normal metabolic functioning of the body. |