| Desc: |
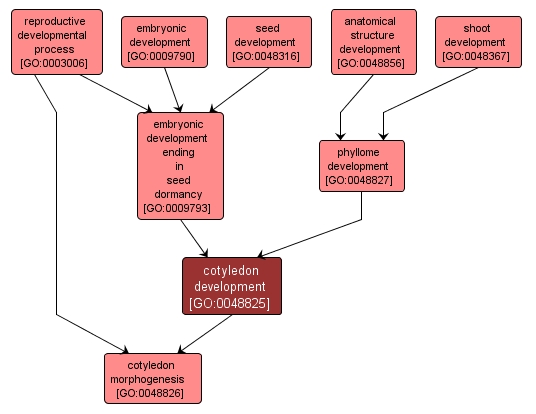
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the cotyledon over time, from its formation to the mature structure. The cotyledon is the modified leaf (seed leaf), found as part of the embryo in plant seeds. It is involved in either storage or absorption of food reserves. Dicotyledonous seeds contain two cotyledons, while monocotyledonous seeds contain only one. The cotyledons may appear above ground and show photosynthetic activity in the seedling. |