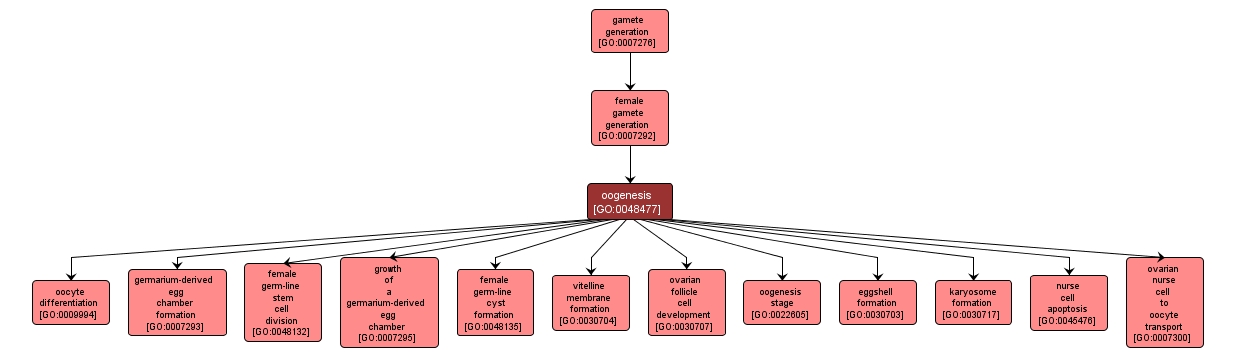
GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
oogenesis |
| Acc: |
GO:0048477 |
| Aspect: |
Biological Process |
| Desc: |
The complete process of formation and maturation of an ovum or female gamete from a primordial female germ cell. Examples of this process are found in Mus musculus and Drosophila melanogaster. |
Synonyms:
- GO:0048157
- GO:0009993
- ovum development
|
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|