GO TERM SUMMARY
|
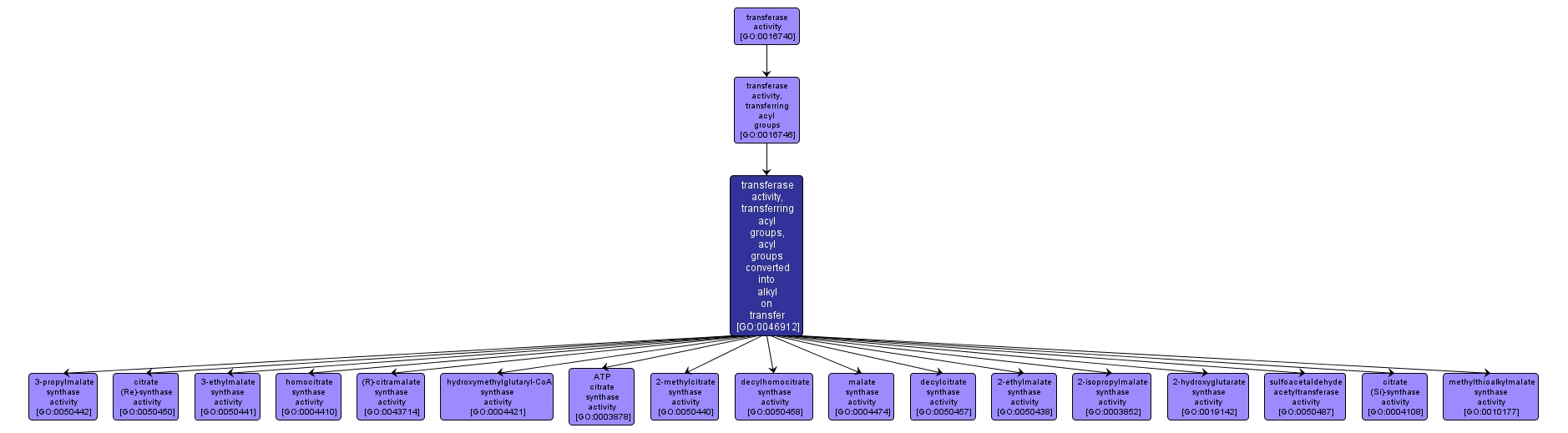
| Name: |
transferase activity, transferring acyl groups, acyl groups converted into alkyl on transfer |
| Acc: |
GO:0046912 |
| Aspect: |
Molecular Function |
| Desc: |
Catalysis of the transfer of an acyl group from one compound (donor) to another (acceptor), with the acyl group being converted into alkyl on transfer. |
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|