| Desc: |
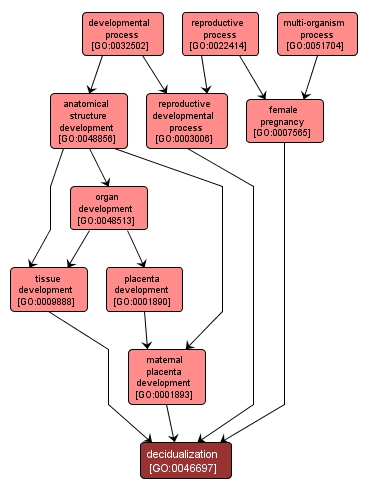
The cellular and vascular changes occurring in the endometrium of the pregnant uterus just after the onset of blastocyst implantation. This process involves the proliferation and differentiation of the fibroblast-like endometrial stromal cells into large, polyploid decidual cells that eventually form the maternal component of the placenta. |