GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
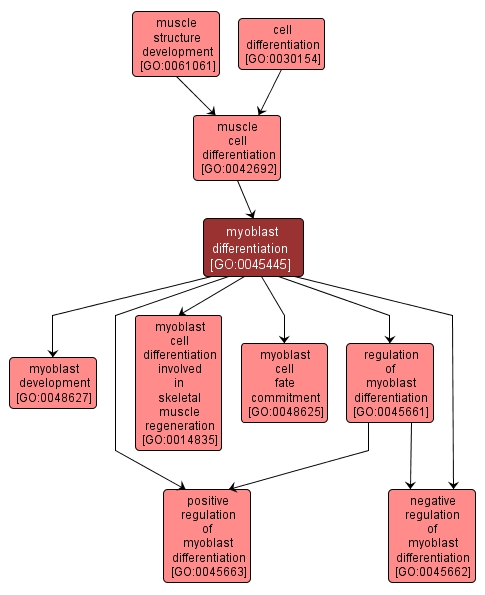
myoblast differentiation |
| Acc: |
GO:0045445 |
| Aspect: |
Biological Process |
| Desc: |
The process whereby a relatively unspecialized cell acquires specialized features of a myoblast. A myoblast is a mononucleate cell type that, by fusion with other myoblasts, gives rise to the myotubes that eventually develop into striated muscle fibers. |
Synonyms:
- myoblast cell differentiation
|
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|