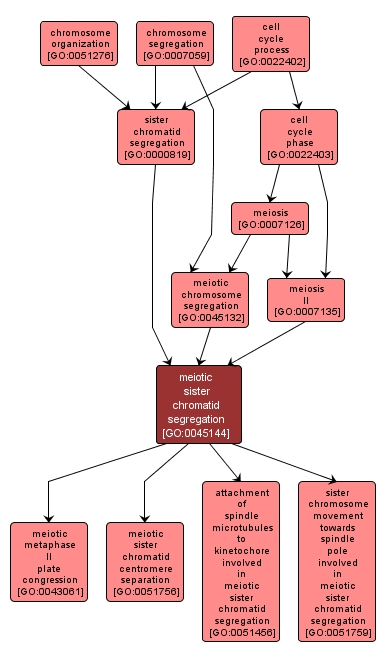
GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
meiotic sister chromatid segregation |
| Acc: |
GO:0045144 |
| Aspect: |
Biological Process |
| Desc: |
The cell cycle process whereby sister chromatids are organized and then physically separated and randomly apportioned to two sets during the second division of the meiotic cell cycle. |
Synonyms:
- meiosis II, chromosome segregation
|
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|