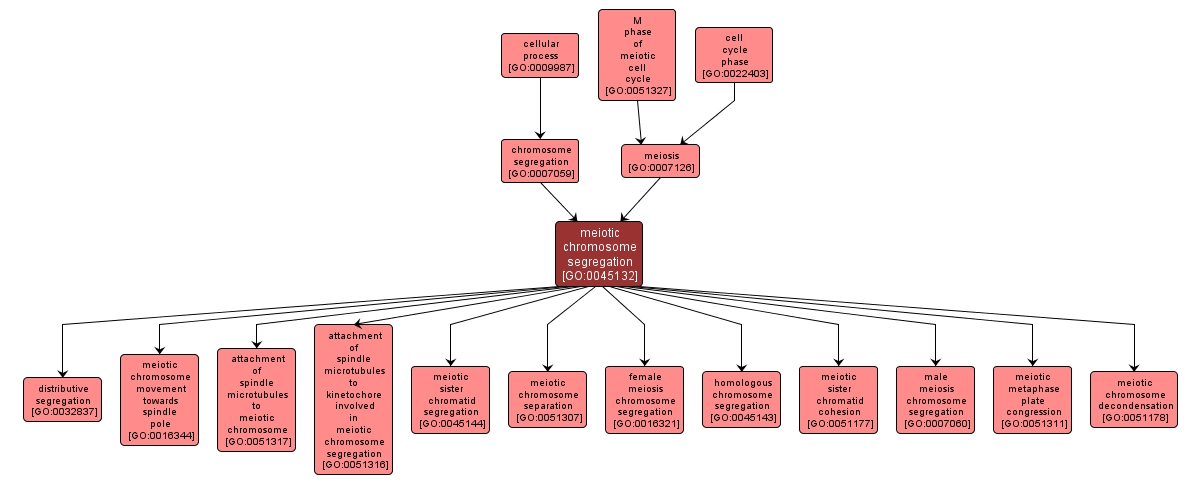
GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
meiotic chromosome segregation |
| Acc: |
GO:0045132 |
| Aspect: |
Biological Process |
| Desc: |
The process by which genetic material, in the form of chromosomes, is organized into specific structures and then physically separated and apportioned to two or more sets during M phase of the meiotic cell cycle. |
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|