GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
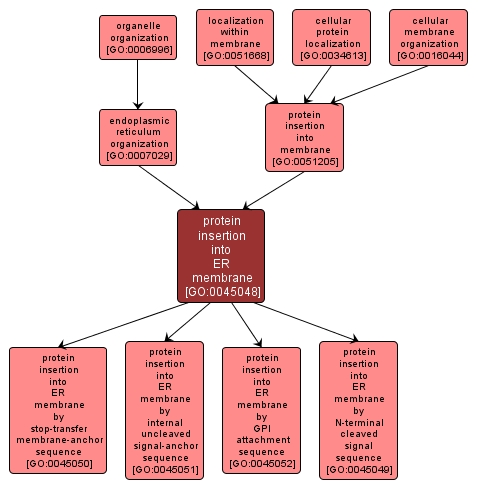
protein insertion into ER membrane |
| Acc: |
GO:0045048 |
| Aspect: |
Biological Process |
| Desc: |
The process by which a protein is incorporated into an endoplasmic reticulum (ER) membrane. It depends on specific topogenic sequences of amino acids that ensure that a protein acquires the proper orientation during its insertion into the ER membrane. |
Synonyms:
- protein-endoplasmic reticulum insertion
- integral ER membrane protein positioning
- positioning of protein in ER membrane
- integral ER membrane protein localization
- protein-ER insertion
- protein insertion into endoplasmic reticulum membrane
- localization of protein in ER membrane
|