| Desc: |
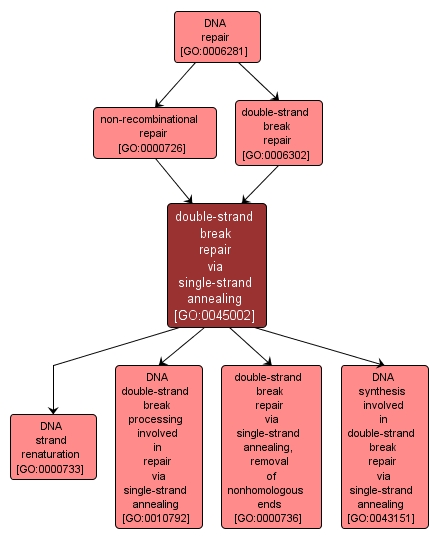
Repair of a DSB made between two repeated sequences oriented in the same direction occurs primarily by the single strand annealing pathway. The ends of the break are processed by a 5' to 3' exonuclease, exposing complementary single-strand regions of the direct repeats that can anneal, resulting in a deletion of the unique DNA between the direct repeats. |