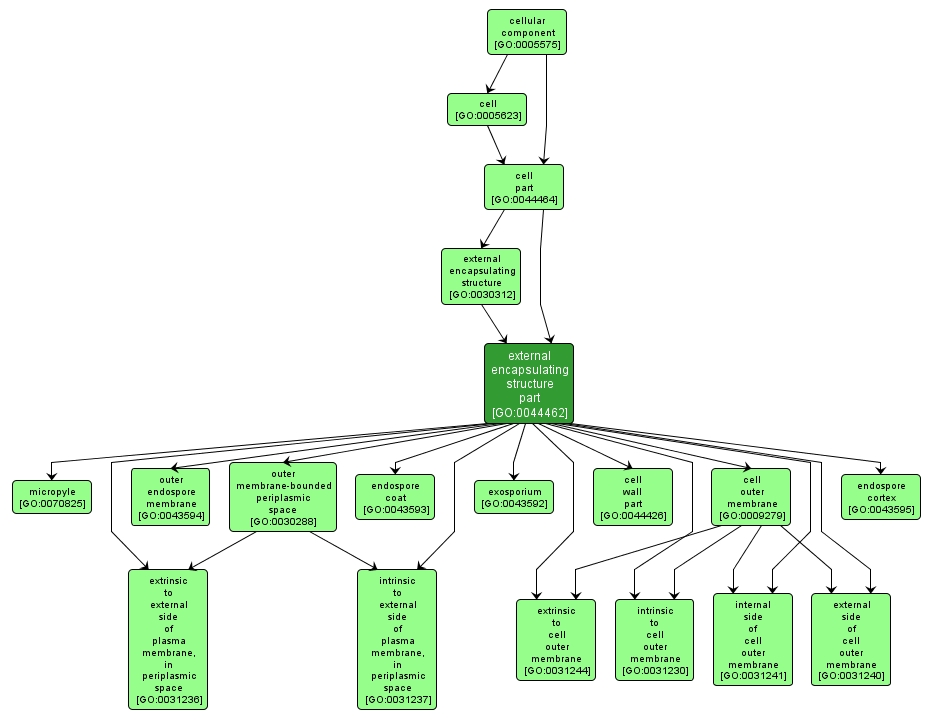
GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
external encapsulating structure part |
| Acc: |
GO:0044462 |
| Aspect: |
Cellular Component |
| Desc: |
Any constituent part of an external encapsulating structure, a structure that lies outside the plasma membrane and surrounds the entire cell. |
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|