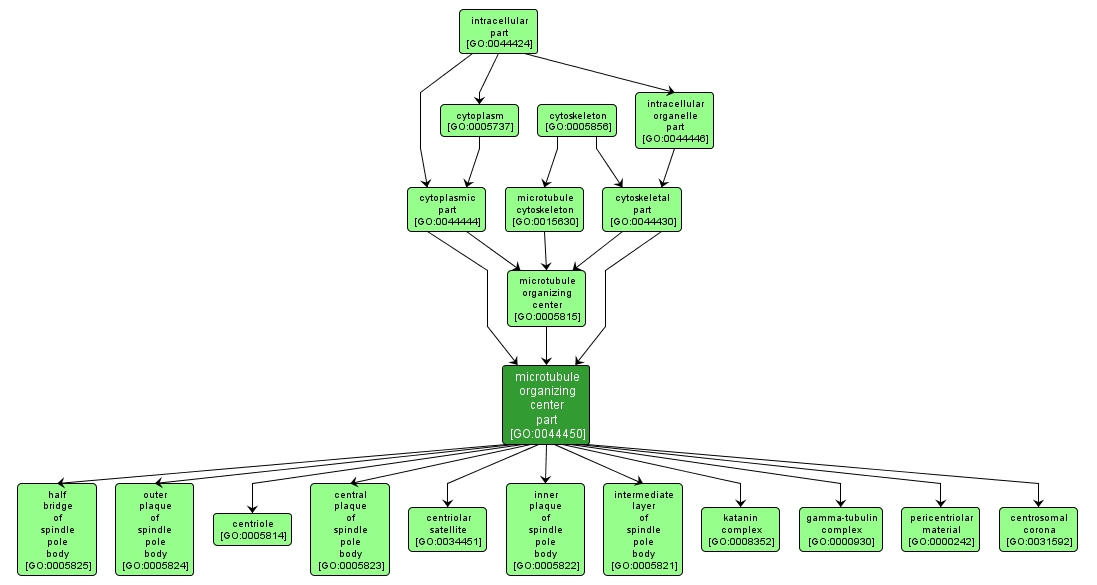
GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
microtubule organizing center part |
| Acc: |
GO:0044450 |
| Aspect: |
Cellular Component |
| Desc: |
Any constituent part of a microtubule organizing center, a region in a eukaryotic cell, such as a centrosome or basal body, from which microtubules grow. |
Synonyms:
- microtubule organizing centre component
- MTOC component
|
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|