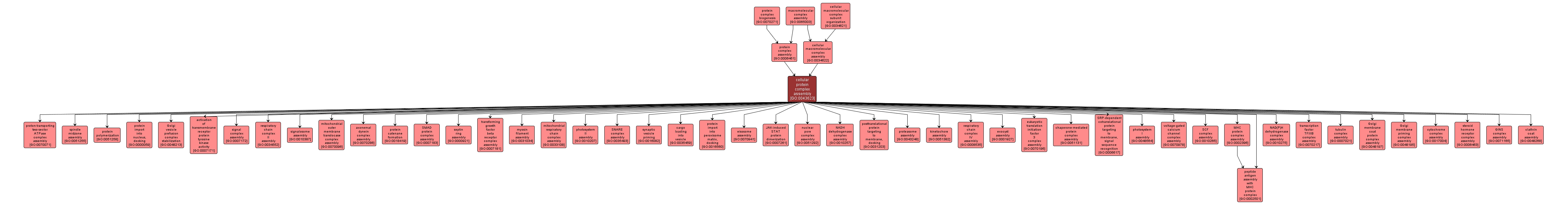
GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
cellular protein complex assembly |
| Acc: |
GO:0043623 |
| Aspect: |
Biological Process |
| Desc: |
The aggregation, arrangement and bonding together of a set of components to form a protein complex, occurring at the level of an individual cell. |
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|