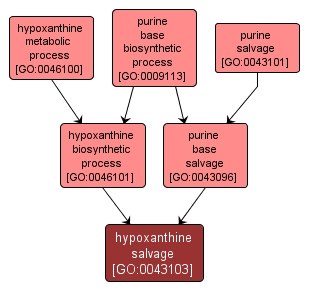
GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
hypoxanthine salvage |
| Acc: |
GO:0043103 |
| Aspect: |
Biological Process |
| Desc: |
Any process that generates hypoxanthine, 6-hydroxy purine, from derivatives of it without de novo synthesis. |
Synonyms:
- guanine, xanthine and their nucleoside salvage
- adenine, hypoxanthine and their nucleoside salvage
|
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|