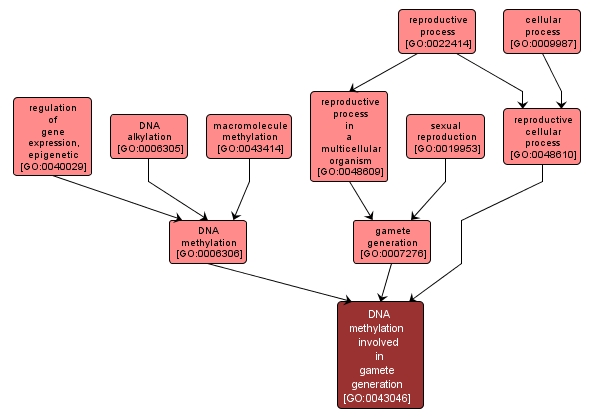
GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
DNA methylation involved in gamete generation |
| Acc: |
GO:0043046 |
| Aspect: |
Biological Process |
| Desc: |
The covalent transfer of a methyl group to C-5 of cytosine that contributes to the establishment of DNA methylation patterns in the gamete. |
| Synonyms:
|
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|