GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
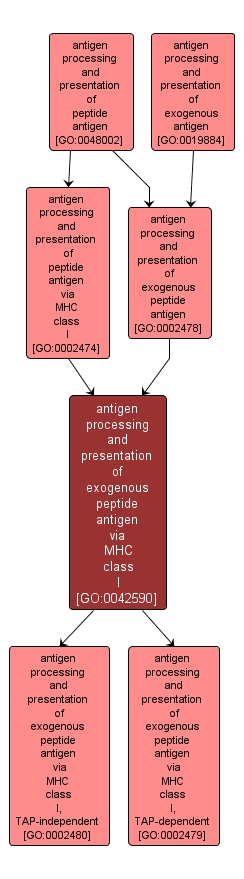
antigen processing and presentation of exogenous peptide antigen via MHC class I |
| Acc: |
GO:0042590 |
| Aspect: |
Biological Process |
| Desc: |
The process by which an antigen-presenting cell expresses a peptide antigen of exogenous origin on its cell surface in association with an MHC class I protein complex. The peptide antigen is typically, but not always, processed from a whole protein. Class I here refers to classical class I molecules. |
Synonyms:
- cross-priming
- exogenous peptide antigen processing and presentation via MHC class I
- cross priming
- cross-presentation
- antigen presentation, exogenous antigen via major histocompatibility complex class I
- cross presentation
- antigen presentation, exogenous antigen via MHC class I
|
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|