| Desc: |
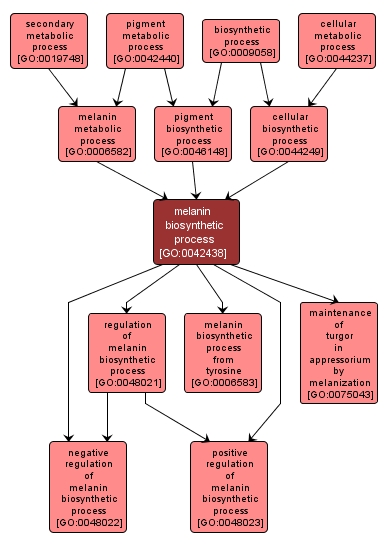
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of melanins, pigments largely of animal origin. High molecular weight polymers of indole quinone, they are irregular polymeric structures and are divided into three groups: allomelanins in the plant kingdom and eumelanins and phaeomelanins in the animal kingdom. |