| Desc: |
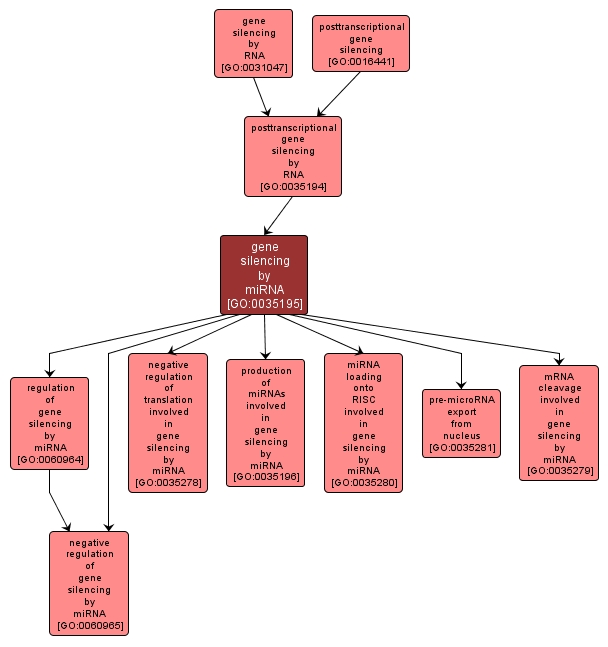
Downregulation of gene expression through the action of microRNAs (miRNAs), endogenous 21-24 nucleotide small RNAs processed from stem-loop RNA precursors (pre-miRNAs). Once incorporated into a RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC), miRNAs can downregulate gene expression by either of two posttranscriptional mechanisms: mRNA cleavage or translational repression. |