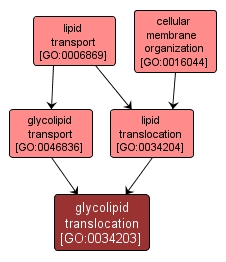
GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
glycolipid translocation |
| Acc: |
GO:0034203 |
| Aspect: |
Biological Process |
| Desc: |
The translocation, or flipping, of glycolipid molecules from one monolayer of a membrane bilayer to the opposite monolayer. |
| Synonyms:
|
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|