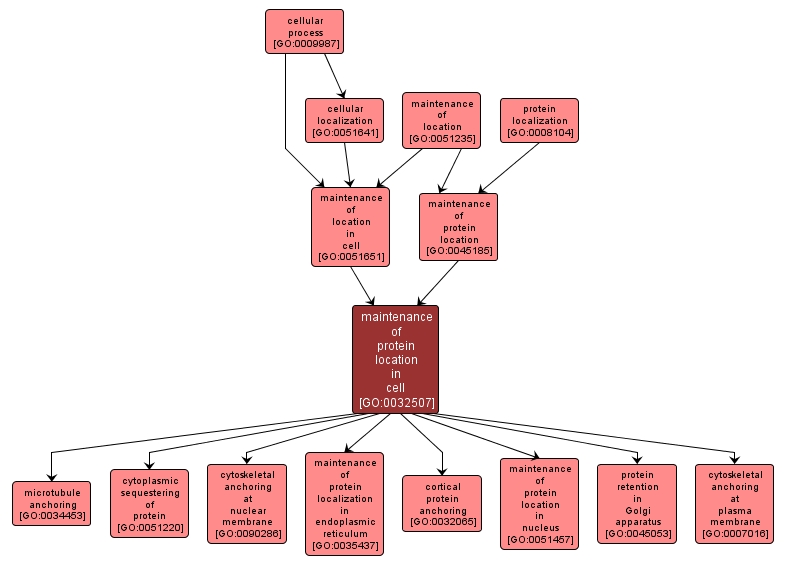
GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
maintenance of protein location in cell |
| Acc: |
GO:0032507 |
| Aspect: |
Biological Process |
| Desc: |
Any process by which a protein is maintained in a specific location within, or in the membrane of, a cell, and is prevented from moving elsewhere. |
Synonyms:
- maintenance of protein localization in cell
|
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|