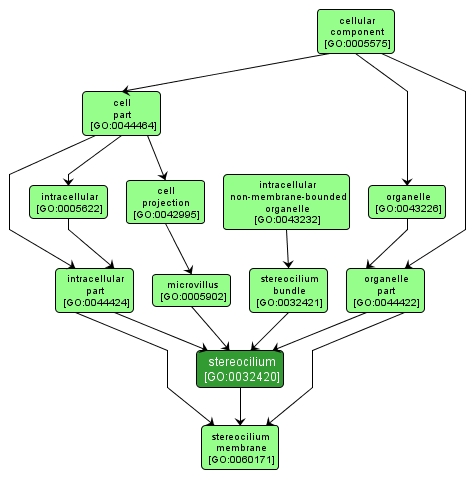
GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
stereocilium |
| Acc: |
GO:0032420 |
| Aspect: |
Cellular Component |
| Desc: |
An actin-based protrusion from the apical surface of auditory and vestibular hair cells. Bundles of stereocilia act as mechanosensory organelles. |
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|