GO TERM SUMMARY
|
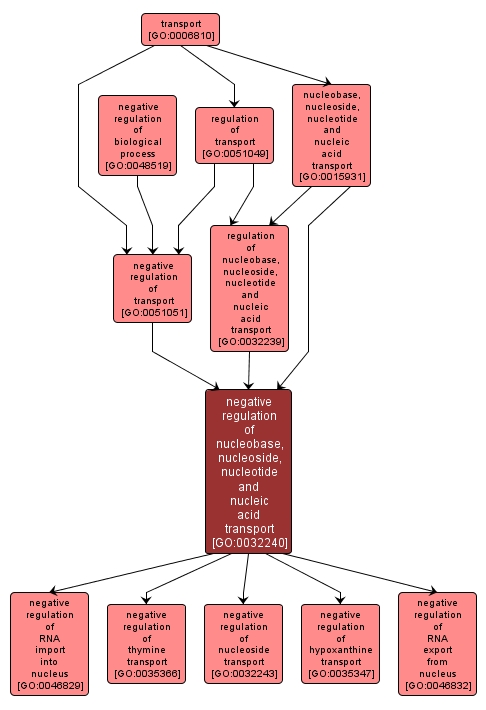
| Name: |
negative regulation of nucleobase, nucleoside, nucleotide and nucleic acid transport |
| Acc: |
GO:0032240 |
| Aspect: |
Biological Process |
| Desc: |
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of the directed movement of nucleobases, nucleosides, nucleotides and nucleic acids, into, out of, within or between cells by means of some external agent such as a transporter or pore. |
Synonyms:
- down-regulation of nucleobase, nucleoside, nucleotide and nucleic acid transport
- inhibition of nucleobase, nucleoside, nucleotide and nucleic acid transport
- down regulation of nucleobase, nucleoside, nucleotide and nucleic acid transport
- downregulation of nucleobase, nucleoside, nucleotide and nucleic acid transport
|
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|