GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
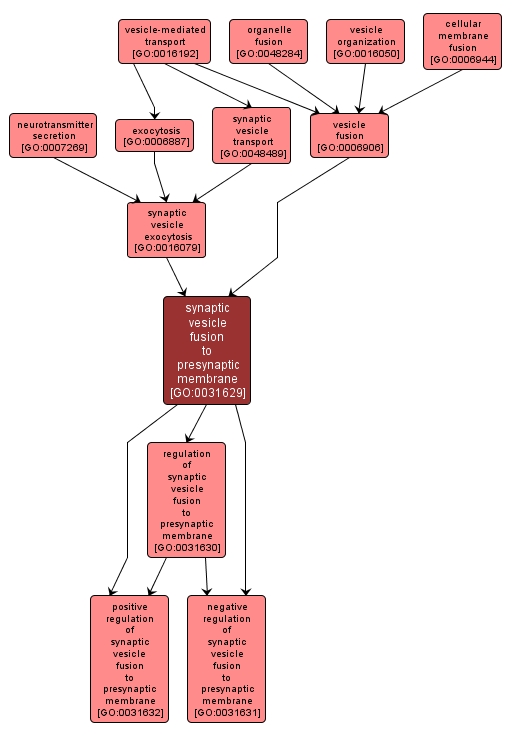
synaptic vesicle fusion to presynaptic membrane |
| Acc: |
GO:0031629 |
| Aspect: |
Biological Process |
| Desc: |
Fusion of the membrane of a synaptic vesicle with its target presynaptic membrane, thereby releasing its cargo neurotransmitters into the synaptic cleft. |
Synonyms:
- synaptic vesicle internalization
- synaptic vesicle fusion
|
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|