| Desc: |
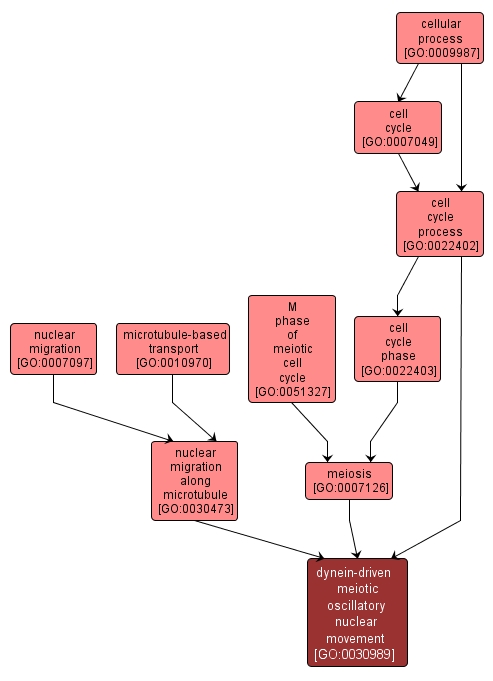
The cell cycle process whereby oscillatory movement of the nucleus during meiotic prophase I occurs. This oscillatory movement is led by an astral microtubule array emanating from the spindle pole body, and driven by the microtubule motor cytoplasmic dynein. It is known to play a central role in meiotic recombination and homologous chromosome pairing; as observed in S. pombe. |