GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
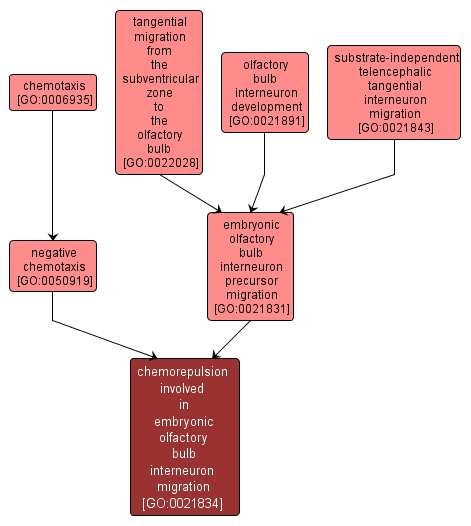
chemorepulsion involved in embryonic olfactory bulb interneuron migration |
| Acc: |
GO:0021834 |
| Aspect: |
Biological Process |
| Desc: |
The creation and reception of signals that guide olfactory bulb interneurons down concentration gradients towards the olfactory bulb. |
Synonyms:
- negative chemotaxis involved in embryonic olfactory bulb interneuron migration
|
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|