| Desc: |
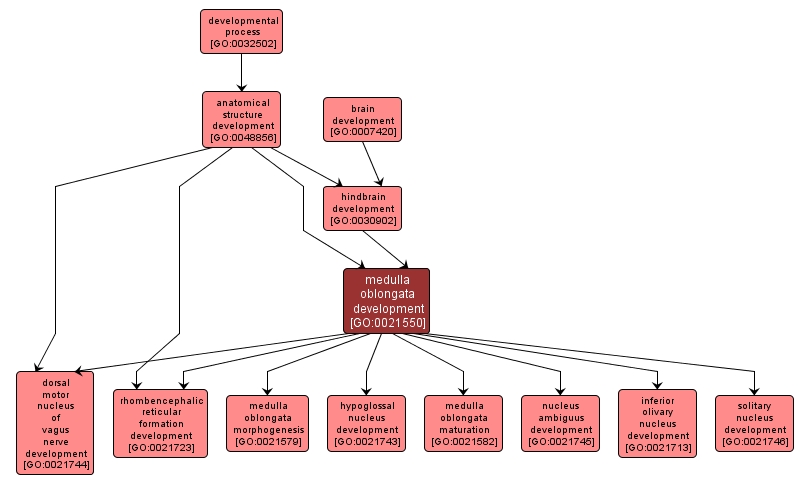
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the medulla oblongata over time, from its formation to the mature structure. The medulla oblongata lies directly above the spinal cord and controls vital autonomic functions such as digestion, breathing and the control of heart rate. |