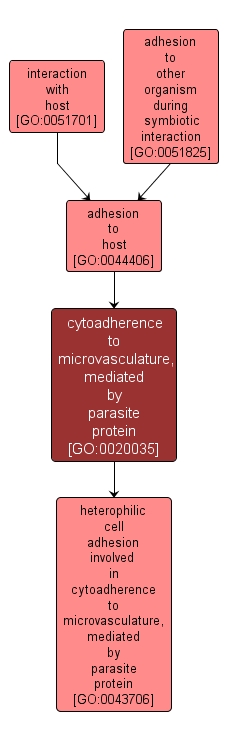
GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
cytoadherence to microvasculature, mediated by parasite protein |
| Acc: |
GO:0020035 |
| Aspect: |
Biological Process |
| Desc: |
The adherence of parasite-infected erythrocytes to microvascular endothelium via parasite proteins embedded in the membrane of the erythrocyte. |
Synonyms:
- parasite-protein-mediated cytoadherence to microvasculature
- symbiont-protein-mediated cytoadherence to microvasculature
- cytoadherence to microvasculature, mediated by symbiont protein
|
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|