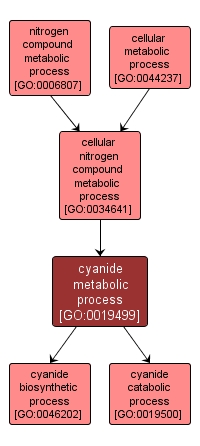
GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
cyanide metabolic process |
| Acc: |
GO:0019499 |
| Aspect: |
Biological Process |
| Desc: |
The chemical reactions and pathways involving cyanide, NC-, the anion of hydrocyanic acid. Cyanide is a potent inhibitor of respiration, reacting with the ferric form of cytochrome aa3 and thus blocking the electron transport chain. |
| Synonyms:
|
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|