GO TERM SUMMARY
|
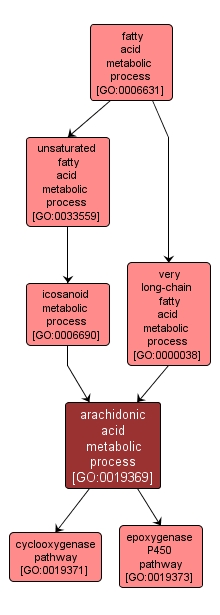
| Name: |
arachidonic acid metabolic process |
| Acc: |
GO:0019369 |
| Aspect: |
Biological Process |
| Desc: |
The chemical reactions and pathways involving arachidonic acid, a straight chain fatty acid with 20 carbon atoms and four double bonds per molecule. Arachidonic acid is the all-Z-(5,8,11,14)-isomer. |
Synonyms:
- arachidonic acid metabolism
|
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|